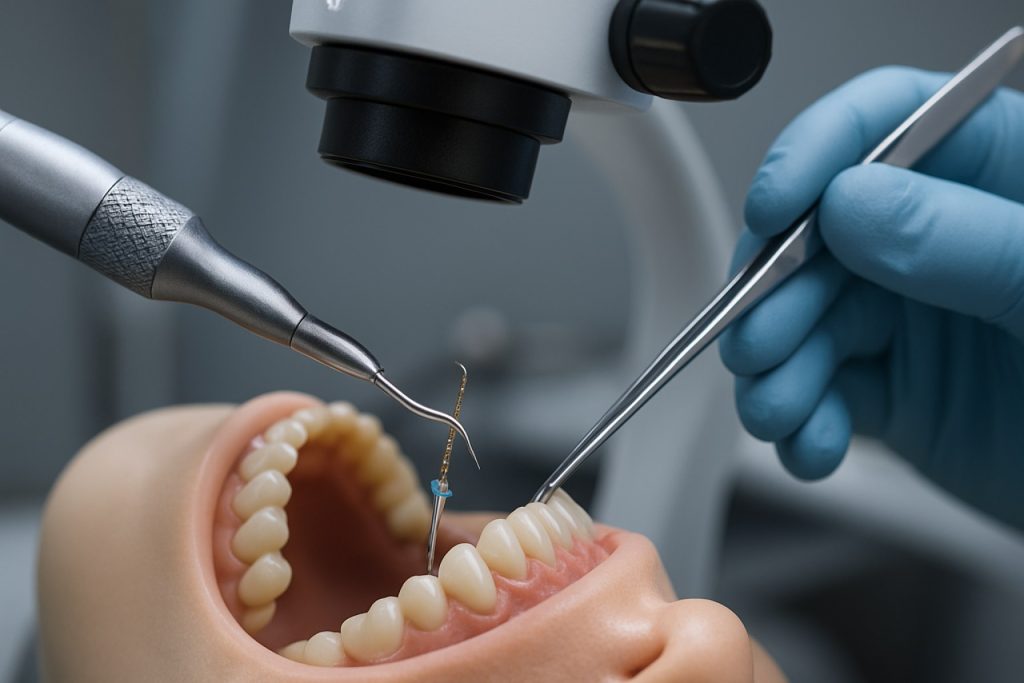
Endodontic Microsurgery Instrumentation in 2025: How Advanced Tools and Techniques Are Transforming Root Canal Success. Explore Market Growth, Technology Shifts, and the Future of Precision Dentistry.
- Executive Summary: Key Trends and Market Drivers in 2025
- Market Size and Forecast (2025–2029): Growth Projections and Regional Analysis
- Technological Innovations: Microscopes, Ultrasonics, and Micro-Instruments
- Leading Manufacturers and Product Portfolios (e.g., dentsplysirona.com, kerrdental.com, seilerinst.com)
- Adoption Trends: Clinical Practice and Training in Endodontic Microsurgery
- Regulatory Landscape and Quality Standards (e.g., aae.org, ada.org)
- Competitive Landscape: Mergers, Partnerships, and New Entrants
- Challenges and Barriers: Cost, Accessibility, and Practitioner Expertise
- Future Outlook: Emerging Technologies and Market Opportunities Through 2029
- Appendix: Methodology, Glossary, and Company Profiles
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: Key Trends and Market Drivers in 2025
The endodontic microsurgery instrumentation market in 2025 is characterized by rapid technological advancements, increased adoption of minimally invasive techniques, and a growing emphasis on precision and patient outcomes. The integration of enhanced visualization tools, such as dental operating microscopes and high-definition imaging systems, is a defining trend, enabling clinicians to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and efficiency. Leading manufacturers, including Carl Zeiss Meditec AG and Leica Microsystems, continue to innovate in optical technologies, offering microscopes with improved ergonomics, digital connectivity, and integrated documentation features tailored for endodontic applications.
Another key driver is the evolution of microsurgical instruments themselves. Companies such as Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Corporation are expanding their portfolios with micro-scaled ultrasonic tips, retrograde filling instruments, and biocompatible root-end filling materials. These advancements are designed to enhance tactile control, reduce tissue trauma, and improve healing rates. The use of nickel-titanium alloys and surface coatings is also increasing, providing greater durability and flexibility for intricate procedures.
Digital integration is reshaping the workflow in endodontic microsurgery. The adoption of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and digital planning software is becoming standard, allowing for precise preoperative assessment and real-time intraoperative guidance. Companies like Planmeca and Carestream Dental are at the forefront, offering advanced imaging solutions that seamlessly interface with surgical navigation systems. This trend is expected to accelerate, with artificial intelligence and machine learning poised to further enhance diagnostic accuracy and procedural predictability in the coming years.
Market growth is also fueled by the rising prevalence of dental diseases, increased patient awareness, and a global shift toward tooth preservation over extraction. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is witnessing robust demand due to expanding dental infrastructure and a growing base of trained endodontists. Regulatory support for innovative devices and materials, as seen in the United States and European Union, is facilitating faster product approvals and market entry for new technologies.
Looking ahead, the endodontic microsurgery instrumentation sector is expected to maintain strong momentum, driven by ongoing R&D investments, cross-disciplinary collaborations, and the continuous push for minimally invasive, patient-centered care. The next few years will likely see further miniaturization of instruments, smarter integration of digital tools, and broader accessibility of advanced microsurgical solutions worldwide.
Market Size and Forecast (2025–2029): Growth Projections and Regional Analysis
The global market for endodontic microsurgery instrumentation is poised for steady growth from 2025 through 2029, driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive dental procedures, technological advancements, and expanding dental care infrastructure in both developed and emerging regions. The market encompasses a range of specialized instruments, including microsurgical mirrors, ultrasonic tips, micro-scalpels, micro-forceps, and high-magnification operating microscopes, all essential for precision in endodontic microsurgery.
North America is expected to maintain its leading position in the market, supported by a high prevalence of dental disorders, robust healthcare expenditure, and the presence of major industry players. The United States, in particular, benefits from a well-established dental care system and early adoption of advanced microsurgical tools. Companies such as Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Corporation are prominent in this region, offering a comprehensive portfolio of endodontic microsurgery instruments and investing in research and development to enhance product efficacy and ergonomics.
Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France exhibiting significant market shares due to their advanced dental care infrastructure and growing awareness of the benefits of microsurgical endodontic procedures. The region also benefits from the presence of established manufacturers such as Coltene and VDW Dental, both of which are recognized for their innovation in endodontic instrumentation and strong distribution networks across the continent.
The Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness the fastest growth rate during the forecast period, fueled by rising dental healthcare investments, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing number of dental clinics and hospitals. Countries like China, India, and Japan are at the forefront of this expansion, with local and international manufacturers expanding their presence. Companies such as Microsurgery Dental and Mani, Inc. are actively contributing to the regional market by offering a range of microsurgical instruments tailored to local clinical needs.
Looking ahead, the market outlook remains positive, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected in the mid to high single digits through 2029. Key growth drivers include ongoing product innovation, increasing adoption of digital and magnification technologies, and a rising focus on patient outcomes and procedural efficiency. As dental professionals continue to prioritize precision and minimally invasive techniques, demand for advanced endodontic microsurgery instrumentation is set to rise globally.
Technological Innovations: Microscopes, Ultrasonics, and Micro-Instruments
The landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation is undergoing rapid transformation in 2025, driven by technological innovations in operating microscopes, ultrasonic devices, and micro-instruments. These advancements are enhancing precision, visibility, and clinical outcomes in endodontic procedures.
Operating microscopes have become a cornerstone of modern endodontic microsurgery, offering magnification and illumination that enable clinicians to perform intricate procedures with greater accuracy. Leading manufacturers such as Carl Zeiss Meditec and Leica Microsystems continue to refine their dental microscopes, integrating features like apochromatic optics, LED illumination, and digital imaging capabilities. In 2025, the trend is toward microscopes with ergonomic designs and integrated documentation systems, allowing for real-time recording and sharing of surgical procedures. These innovations not only improve workflow but also facilitate education and remote consultations.
Ultrasonic technology is another area experiencing significant progress. Ultrasonic tips and handpieces, essential for root-end preparation and retrograde filling, are now being engineered for enhanced durability and efficiency. Companies such as Dentsply Sirona and Acteon Group are at the forefront, offering piezoelectric ultrasonic units with precise power modulation and a wide array of specialized tips. In 2025, the focus is on reducing heat generation and improving tactile feedback, which minimizes the risk of iatrogenic damage and increases patient safety.
Micro-instruments, including micro-mirrors, micro-forceps, and micro-scalpels, are being developed with advanced materials such as titanium alloys and high-grade stainless steel to ensure longevity and biocompatibility. Hu-Friedy Group and Kerr Dental are notable for their comprehensive portfolios of endodontic microsurgical instruments. In 2025, instrument miniaturization and ergonomic handle designs are key trends, enabling clinicians to access challenging anatomical areas with minimal tissue trauma.
Looking ahead, the integration of digital technologies—such as augmented reality overlays and artificial intelligence-assisted navigation—into microscopes and surgical units is anticipated to further revolutionize endodontic microsurgery. The next few years are expected to see increased adoption of these smart systems, driven by ongoing R&D investments from industry leaders and the growing demand for minimally invasive, high-precision dental care.
Leading Manufacturers and Product Portfolios (e.g., dentsplysirona.com, kerrdental.com, seilerinst.com)
The landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation in 2025 is shaped by a select group of global manufacturers, each offering comprehensive product portfolios that address the evolving demands of precision, ergonomics, and clinical outcomes. These companies are not only expanding their instrument lines but also integrating advanced materials and digital technologies to enhance surgical efficiency and patient safety.
Dentsply Sirona remains a dominant force in the endodontic sector, with a robust suite of microsurgical instruments and accessories. Their offerings include microsurgical mirrors, ultrasonic tips, micro pluggers, and retrograde filling instruments, all designed for optimal tactile feedback and minimal tissue trauma. Dentsply Sirona’s focus on research and clinician feedback has led to iterative improvements in instrument design, such as enhanced grip ergonomics and corrosion-resistant alloys. The company also invests in digital workflow integration, supporting clinicians with imaging and navigation systems that complement their surgical kits (Dentsply Sirona).
Kerr Dental, a subsidiary of Envista Holdings, is another key player, recognized for its SybronEndo brand. Kerr’s microsurgical product line features precision-engineered micro scissors, forceps, and curettes, as well as ultrasonic surgical units tailored for apical surgery. Their instruments are manufactured with high-grade stainless steel and titanium, ensuring durability and sterilization compatibility. Kerr Dental’s commitment to clinician education and product innovation is evident in their ongoing collaborations with endodontic specialists to refine instrument shapes and sizes for specific surgical scenarios (Kerr Dental).
In the field of dental microscopy, Seiler Instrument stands out for its high-definition surgical microscopes, which are increasingly considered standard equipment in endodontic microsurgery suites. Seiler’s microscopes offer advanced LED illumination, multiple magnification levels, and ergonomic designs that reduce operator fatigue during lengthy procedures. The integration of digital imaging and video documentation capabilities is a notable trend, supporting both clinical documentation and remote consultation (Seiler Instrument).
Other notable manufacturers include Hu-Friedy, known for its precision hand instruments and micro-surgical kits, and Brasseler USA, which supplies a range of microsurgical burs and ultrasonic tips. Both companies emphasize quality control and clinician-driven product development, ensuring their portfolios remain aligned with the latest procedural protocols and material science advancements (Hu-Friedy, Brasseler USA).
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see further integration of digital technologies, such as augmented reality guidance and AI-assisted imaging, into endodontic microsurgery instrumentation. Leading manufacturers are likely to expand their portfolios with smart instruments and connected devices, reinforcing their roles as innovation drivers in the global dental market.
Adoption Trends: Clinical Practice and Training in Endodontic Microsurgery
The adoption of advanced instrumentation in endodontic microsurgery is accelerating in 2025, driven by both technological innovation and evolving clinical protocols. The integration of high-magnification operating microscopes, ultrasonic surgical tips, and biocompatible retrograde filling materials is now considered standard in many specialist practices. This shift is supported by the increasing availability of compact, ergonomically designed microscopes and enhanced illumination systems, which facilitate precision and reduce operator fatigue. Leading manufacturers such as Carl Zeiss Meditec and Leica Microsystems continue to refine optical systems, offering features like apochromatic lenses and integrated digital imaging, which are being rapidly adopted in postgraduate training and private clinics.
Ultrasonic instrumentation, particularly for root-end preparation, has seen significant improvements in tip design and material durability. Companies like Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Dental have introduced new lines of ultrasonic surgical tips with enhanced cutting efficiency and reduced risk of microfractures. These innovations are increasingly incorporated into endodontic residency curricula and hands-on workshops, reflecting a broader trend toward evidence-based microsurgical protocols.
The adoption of bioceramic materials for root-end filling, such as those produced by Brasseler USA and FKG Dentaire, is also rising. These materials offer superior sealing ability and biocompatibility compared to traditional amalgam or intermediate restorative materials. Their use is now recommended in updated clinical guidelines and is being emphasized in continuing education programs for practicing endodontists.
Digital integration is another key trend. The use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) for preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation is becoming routine, with companies like Planmeca and Carestream Dental providing advanced imaging platforms tailored for endodontic applications. This digital workflow is increasingly taught in dental schools and specialist training centers, ensuring new graduates are proficient in both hardware and software aspects of microsurgical instrumentation.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see further miniaturization of instruments, integration of artificial intelligence for image analysis, and the development of smart surgical tools with real-time feedback. The ongoing collaboration between manufacturers, academic institutions, and professional bodies is likely to accelerate the adoption of these innovations, shaping the future landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation and training.
Regulatory Landscape and Quality Standards (e.g., aae.org, ada.org)
The regulatory landscape and quality standards for endodontic microsurgery instrumentation are evolving rapidly as technological advancements and clinical demands shape the sector in 2025 and beyond. Regulatory oversight is primarily governed by national and international bodies, with the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) setting the baseline for device approval, safety, and post-market surveillance. In the U.S., endodontic instruments are classified as medical devices, subject to rigorous premarket notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) processes, depending on their risk profile. The FDA mandates compliance with Quality System Regulations (QSR), which encompass design controls, manufacturing practices, and post-market vigilance to ensure patient safety and device efficacy.
Professional organizations such as the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) and the American Dental Association (ADA) play a pivotal role in establishing and updating clinical guidelines and best practices for the use of microsurgical instruments. The AAE, for instance, regularly publishes position statements and clinical practice guidelines that inform practitioners about the latest evidence-based protocols for endodontic microsurgery, including recommendations on instrument selection, sterilization, and maintenance. The ADA, through its Standards Committee on Dental Products, collaborates with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to develop and revise standards such as ISO 3630 for endodontic instruments, ensuring global harmonization of quality benchmarks.
Manufacturers of endodontic microsurgery instruments, including leading companies like Dentsply Sirona, Kerr Dental, and Coltene, are required to adhere to these regulatory and quality frameworks. These companies invest heavily in research and development to meet or exceed evolving standards, often participating in industry working groups and standard-setting initiatives. For example, Dentsply Sirona and Coltene are known for their active roles in advancing instrument design and collaborating with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and innovation.
Looking ahead, the regulatory environment is expected to become more stringent, with increased emphasis on digital traceability, unique device identification (UDI), and real-world performance data. The integration of digital technologies, such as smart tracking and AI-assisted quality control, is anticipated to further enhance compliance and patient safety. Additionally, sustainability and environmental considerations are gaining prominence, prompting regulators and industry leaders to explore eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes for endodontic instruments. As these trends unfold, ongoing collaboration between regulatory agencies, professional organizations, and manufacturers will be essential to uphold the highest standards of care in endodontic microsurgery instrumentation.
Competitive Landscape: Mergers, Partnerships, and New Entrants
The competitive landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation in 2025 is characterized by strategic mergers, targeted partnerships, and the emergence of new entrants, all aiming to address the growing demand for precision and efficiency in endodontic procedures. Established industry leaders are consolidating their positions through acquisitions and collaborations, while innovative startups are entering the market with disruptive technologies.
One of the most significant trends is the consolidation among major dental equipment manufacturers. Dentsply Sirona, a global leader in dental solutions, has continued to expand its endodontic portfolio through targeted acquisitions and partnerships, focusing on integrating advanced imaging and microsurgical tools. Similarly, Kerr Dental, part of Envista Holdings, has strengthened its position by collaborating with technology firms to enhance the digital integration of their endodontic instrumentation lines.
In 2024 and into 2025, COLTENE has pursued strategic partnerships with digital imaging companies to develop more precise navigation systems for microsurgery, aiming to improve clinical outcomes and workflow efficiency. Brasseler USA has also expanded its microsurgical instrument offerings, leveraging partnerships with academic institutions to drive innovation in instrument design and ergonomics.
The sector is also witnessing the entry of new players, particularly startups specializing in robotics, AI-driven navigation, and miniaturized surgical tools. These entrants are often supported by venture capital and are collaborating with established dental manufacturers to accelerate commercialization. For example, several European and North American startups have announced partnerships with established brands to co-develop next-generation microsurgical handpieces and visualization systems.
Additionally, the competitive landscape is being shaped by cross-industry collaborations. Medical device companies with expertise in microsurgery outside of dentistry are entering the endodontic space, bringing advanced materials and precision engineering to the development of new instruments. This trend is expected to intensify over the next few years as the boundaries between dental and broader medical device innovation continue to blur.
Looking ahead, the market is likely to see further consolidation as established players seek to acquire innovative startups and expand their technological capabilities. At the same time, ongoing partnerships between manufacturers, technology firms, and academic institutions will drive the development of more sophisticated, user-friendly, and digitally integrated endodontic microsurgery instruments, shaping the competitive dynamics through 2025 and beyond.
Challenges and Barriers: Cost, Accessibility, and Practitioner Expertise
Endodontic microsurgery instrumentation has advanced significantly, yet several challenges and barriers persist as of 2025, particularly regarding cost, accessibility, and practitioner expertise. These factors continue to shape the adoption and effective utilization of modern microsurgical tools in endodontics.
Cost remains a primary barrier. High-quality surgical microscopes, ultrasonic tips, micro-instruments, and supporting technologies such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems represent substantial investments for dental practices. Leading manufacturers like Carl Zeiss Meditec and Leica Microsystems offer state-of-the-art dental microscopes, but their advanced optics and ergonomic features come at a premium. Similarly, companies such as Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Dental supply specialized ultrasonic surgical tips and micro-instruments, which, while essential for precision, add to the overall procedural cost. For many smaller clinics and practitioners in developing regions, these expenses can be prohibitive, limiting widespread adoption.
Accessibility to advanced endodontic microsurgery instrumentation is uneven globally. While dental centers in North America, Western Europe, and parts of East Asia have relatively easy access to the latest equipment, practitioners in low- and middle-income countries often face supply chain challenges and limited local distribution networks. Companies like Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Dental have expanded their global reach, but logistical and regulatory hurdles persist in certain regions, affecting the timely and affordable availability of these instruments.
Practitioner expertise is another significant barrier. The effective use of microsurgical instruments requires advanced training in both the technology and the refined techniques of endodontic microsurgery. While organizations such as the American Association of Endodontists and various dental schools have increased their focus on microsurgical training, there remains a learning curve. Many general practitioners and even some endodontists may lack hands-on experience with the latest microscopes, ultrasonic devices, and micro-instruments, potentially impacting clinical outcomes. The need for ongoing education and certification is expected to grow, with manufacturers and professional bodies investing in workshops, online modules, and simulation-based training.
Looking ahead, the industry is responding with incremental innovations aimed at reducing costs, improving portability, and simplifying user interfaces. However, unless these efforts are matched by broader training initiatives and improved distribution, the challenges of cost, accessibility, and practitioner expertise will likely continue to influence the global landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation over the next few years.
Future Outlook: Emerging Technologies and Market Opportunities Through 2029
The landscape of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation is poised for significant transformation through 2029, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving clinical demands. As of 2025, the integration of digital technologies, enhanced materials, and precision engineering is reshaping both the tools and techniques used in endodontic microsurgery.
One of the most notable trends is the increasing adoption of surgical operating microscopes with advanced optics and digital imaging capabilities. Companies such as Carl Zeiss Meditec AG and Leica Microsystems are at the forefront, offering microscopes that provide superior magnification, illumination, and documentation features. These systems are expected to become more compact, user-friendly, and integrated with augmented reality (AR) overlays, enabling real-time guidance and improved surgical outcomes.
Another area of innovation is the development of microsurgical instruments with enhanced ergonomics and durability. Manufacturers like Dentsply Sirona and Kerr Corporation are investing in high-grade stainless steel and titanium alloys, as well as surface coatings that reduce instrument wear and improve tactile feedback. The next few years are likely to see the introduction of even finer micro-instruments, including ultrasonic tips and retrograde filling devices, designed for minimally invasive procedures and improved patient recovery.
Digital workflow integration is also gaining momentum. The use of 3D-printed surgical guides, based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) data, is expected to become more widespread, allowing for precise localization and access during apical surgery. Companies such as Planmeca and Carestream Dental are expanding their digital imaging and planning solutions, which are increasingly compatible with endodontic microsurgical applications.
Looking ahead, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are anticipated to play a growing role in diagnostics, treatment planning, and intraoperative navigation. AI-powered software could assist clinicians in identifying anatomical variations, predicting surgical challenges, and optimizing instrument selection. This convergence of digital and mechanical innovation is expected to drive market growth and open new opportunities for both established players and emerging startups.
In summary, the future of endodontic microsurgery instrumentation through 2029 will be characterized by smarter, more precise, and digitally integrated solutions. As leading manufacturers continue to invest in R&D and clinicians demand higher standards of care, the sector is set for robust expansion and technological evolution.
Appendix: Methodology, Glossary, and Company Profiles
Appendix: Methodology, Glossary, and Company Profiles
Methodology
This section outlines the research approach used to analyze the endodontic microsurgery instrumentation sector for 2025 and the near future. Primary data was gathered from official manufacturer and supplier websites, regulatory filings, and industry association publications. Secondary data included technical documentation, product catalogs, and press releases from leading companies. The analysis focused on product innovation, market presence, and strategic developments among key players. Only information from direct industry sources was considered to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Glossary
- Endodontic Microsurgery: A specialized dental procedure involving surgical intervention at the root tip (apex) of a tooth, often using a dental operating microscope for enhanced precision.
- Microsurgical Instruments: Precision tools designed for use under magnification, including micro-scalpels, micro-mirrors, ultrasonic tips, and micro-forceps.
- Ultrasonic Tips: Attachments for ultrasonic handpieces used to remove root-end fillings or prepare root-end cavities during microsurgery.
- Retrograde Filling: A technique where filling material is placed at the root tip after apical resection to seal the canal.
- Dental Operating Microscope (DOM): An optical device providing high magnification and illumination, essential for modern endodontic microsurgery.
Company Profiles
- Dentsply Sirona: A global leader in dental technology, Dentsply Sirona offers a comprehensive range of endodontic instruments, including ultrasonic systems, micro-instruments, and dental operating microscopes. The company is known for continuous innovation and integration of digital workflows in endodontics.
- ZEISS: ZEISS is a renowned manufacturer of optical systems, including dental operating microscopes widely used in endodontic microsurgery. Their microscopes are recognized for superior optics and ergonomic design, supporting precision in minimally invasive procedures.
- Brasseler USA: Brasseler USA specializes in dental and surgical instruments, offering a broad portfolio of endodontic microsurgical tools such as micro-blades, ultrasonic tips, and hand instruments tailored for apical surgery.
- Hu-Friedy (a subsidiary of Cantel Medical): Hu-Friedy is a prominent supplier of dental instruments, including microsurgical kits and specialized forceps for endodontic applications. The company emphasizes instrument durability and clinician ergonomics.
- SybronEndo (a division of Kerr Corporation): Kerr Corporation (SybronEndo) provides advanced endodontic solutions, including ultrasonic systems, micro-instruments, and obturation devices, supporting both conventional and microsurgical endodontic procedures.
- Global Surgical Corporation: Global Surgical Corporation is a key provider of dental operating microscopes, focusing on ergonomic design and optical clarity for endodontic microsurgery.
These companies are expected to drive further innovation in endodontic microsurgery instrumentation through ongoing R&D, product launches, and strategic collaborations in 2025 and beyond.
Sources & References
- Carl Zeiss Meditec AG
- Leica Microsystems
- Dentsply Sirona
- Kerr Corporation
- Planmeca
- Carestream Dental
- Coltene
- VDW Dental
- Mani, Inc.
- Acteon Group
- Hu-Friedy Group
- Seiler Instrument
- Hu-Friedy
- American Association of Endodontists
- American Dental Association
- Dentsply Sirona
- Kerr Dental
- Coltene
- American Association of Endodontists
- Global Surgical Corporation



